Đào tạo & nghiên cứu
DIAGNOSTIC VALUE OF LOOP – MEDIATED ISOTHERMAL AMPLIFICATION ASSAY FOR DETECTION STREPTOCOCCUS AGALACTIAE FROM VAGINAL SWAB COMPARED TO THE REALTIME PCR ASSAY
Van H. Pham [1,2]*; Suyen T. Nguyen [1]*; Quoc V. Nguyen [1,3]; Luan D. Phan [1,3],
Viet Q. Tran [1,3]; Huong T. Pham [1,3]
[1]Vietnam Research and Development Institute of Clinical Microbiolgy, Vietnam
[2]Nam Khoa Biotek Co. Ltd., Vietnam
[3]Phan Chau Trinh University, Vietnam
*First author
|
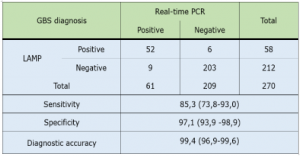
Background Streptococcus agalactiae, also known as group B streptococcus (GBS), is one of the important causes of postpartum and neonatal infection. Therefore, prenatal screening of GBS in the vaginal and rectal swab of the pregnant woman in the last week of pregnancy is greatly contributing to ensuring the health of mothers and babies. Currently, loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) shows advantages over culture by sensitivity and the real-time PCR by simple machines and techniques. Therefore, this test can be considered an alternative to rapid and accurate GBS screening to support emergency decision-making on prophylactic antibiotic use. Objective There are two main objectives: (1) Determining the sensitivity and specificity of the loop-mediated isothermal amplification method compared to the reference real-time PCR method; and (2) Determining the rate of GBS infection in pregnant women by the loop-mediated isothermal amplification method. Materials and Methods The study was designed according to the descriptive cross-sectional method and conducted on 270 samples collected from pregnant women who indicated for GBS screening by real-time PCR method at the laboratory of Nam Khoa Co., Ltd. in the period from November 2022 to May 2023. Total DNA extraction was conducted by the KingFisher automatic extraction and purification system (ThermoFisher Scientific) using a set of chemicals extracted from the Nam Khoa company “DNARNAprep MAGBEAD kit.” The process follows the instructions from the respective manufacturer of the consumables attached to the 200µl sample. The extracted sample after performing a real-time PCR reaction is stored at -20oC. The stored samples will be used for the LAMP assay later. The GBS test by the LAMP PCR method is performed by a kit with six primer pairs designed and provided by the Institute for Clinical Microbiology Research and Development, which is performed to analyze the DNA detection results of GBS on the real-time PCR Rotorgen system. Results and Discussion The study results determined the diagnostic value of the PCR LAMP GBS screening assay when compared to the PCR realtime method with a sensitivity of 85.3% (95% CI: 73.8–93.0), a specificity of 97.1% (95% CI: 93.9–98.9), an accuracy of 94.4% (95% CI: 96.9–99.6), and a Limit of Detection (LOD) of 4 copies per reaction when using 10-fold consecutive dilutions of Streptococcus agalactiae ATCC 11360 NA. The prevalence of GBS infection in pregnant women tested by LAMP PCR was 21.5% (95% CI: 0.17–0.27). In which, the group of pregnant women over 35 years old has the highest infection rate of 26.5%, while the lowest is the 25-35 age group, accounting for 18.7%. In addition, the rate of GBS infection in pregnant women under 35 weeks of age is the highest (30.2%), and the lowest is 16.9% for pregnant women over 37 weeks of age. |
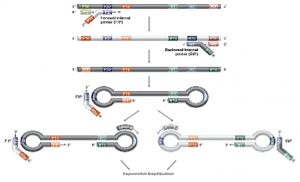
Figure 1: The principle of LAMP (Loop-mediated isothermal amplification) uses 4-6 primers recognizing 6-8 distinct regions of target DNA.
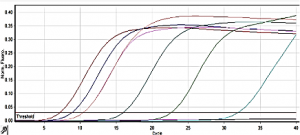
Graph 1: The LOD (limit of detection) of LAMP is 4 copies/reaction volume (same of real-time PCR)
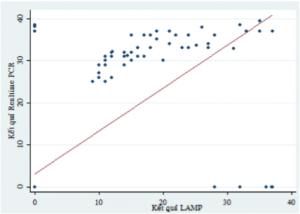
Graph 2: The correlation of the Ct of the GBS detection by LAMP and by real-time PCR
Table 1: The sensitivity, specificity and diagnosis accuracy of LAMP in the detection of GBS
Conclusions The LAMP solution for detecting GBS from vaginal swabs taken from pregnant women was shown in this study to have sensitivity and specificity no different from real-time PCR. Therefore, we hope to develop this solution in clinical microbiology laboratories that do not have PCR facilities to help detect GBS, a very necessary need today. Key words: LAMP, Streptococcus agalactiae
|
REFERENCES
- Curry A, Bookless G, Donaldson K and Knowles SJ. Evaluation of hibergene loopmediated isothermal amplification assay for detection of group B streptococcus in recto-vaginal swabs: a prospective diagnostic accuracy study. Clinical Microbiology and Infection. 2018; 24(10):1066-1069.
- Zietek M, Jaroszewicz-Trzaska J, Szczuko M, Mantiuk R and Celewicz Z. Intrapartum PCR assay is a fast and efficient screening method for Group B Streptococcus detection in pregnancy. Ginekol Pol. 2020; 91(9):549-553. 10.5603/gp.2020.0088.
- Garg N, Ahmad FJ and Kar S. Recent advances in loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) for rapid and efficient detection of pathogens. Curr Res Microb Sci. 2022; 3:100120. 10.1016/j.crmicr.2022.
- Notomi T, Okayama H, Masubuchi H, et al. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000; 28(12):E63. 10.1093.
- Sung J-H, Cha H-H, Lee N-Y, et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for Group B Streptococcus Detection in RectoVaginal Swab: Comparison with Polymerase Chain Reaction Test and Conventional Culture. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(7):1569.