Đào tạo & nghiên cứu
VANCOMYCIN RESISTANCE IN ENTEROCOCCUS AT NGUYEN TRI PHUONG HOSPITAL FROM 2019 TO 2022
Pham Thai Binh [1,2,3,4], Pham Hung Van [3,5], Vo Đuc Chien [2], Nguyen Thi Minh Ha [2]
[1] University pf Medicine and Pharmacy in HCM, [2]Nguyen Tri Phuong Hospital, [3]Vietnam Research and Development Institute of Clinical Microbiology, [4]Nam Khoa Co. LTD, [5]Phan Chau Trinh University
|
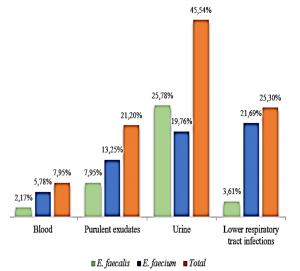
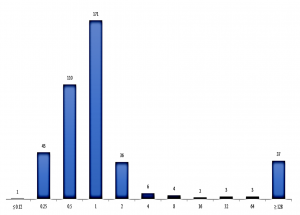
OBJECTIVE To evaluate the antibiotic resistance and vancomycin resistance in Enterococcus isolated from infections at Nguyen Tri Phuong Hospital from 2019 to 2022. METHODS Enterococcus strains isolated from various infections at Nguyen Tri Phuong Hospital from 2019 to 2022. Bacterial strains were identified by routine microbiological laboratory methods. Antibiotics performed by disk diffusion and determined vancomycin MIC by E-test. The antibiotic results were interpreted according to CLSI standards. RESULTS 418 Enterococcus strains were isolated, in which E. faecalis (60.52%) and E. faecium (39.48%). Bacterial strains are derived from infection of urinary tract (45.54%), respiratory tract (25.3%), pus – exudate (21.2%), blood (7.95%). Enterococcus was resistant to erythromycin (81.13%), tetracycline (74.13%), ciprofloxacin (54.40%), levofloxacin (51.12%), penicillin (35.27%), ampicillin (32.59%). There is a difference in antibiotic resistance between E. faecium and E. faecalis, and between vancomycin-resistant and vancomycin-non-resistant Enterococcus strains. In this study, E. faecalis were not resistant to vancomycin, meanwhile vancomycin-resistanct E. faecium were 10.36% with 128µg / mL in MIC90. CONCLUSION Enterococcus is resistant to many antibiotics, including vancomycin, so the infection control strategy and the use of antibiotics to limit the increase in antibiotic resistance is needed. Keywords: vancomycin, Enterococcus, E. faecalis, E. faecium. |
Graph 1: The proportion (%) of Enterococcus according to specimens
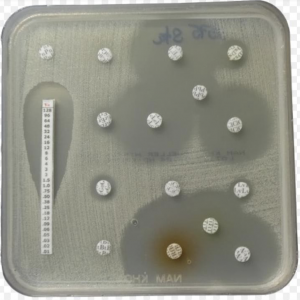
Graph 2: Distribution of MIC values of vancomycin on Enterococcus Picture 1: One of the antibiotic sensitivity testing of Enterococci with Vancomycin sensible |
REFERECES
- Markwart, R., et al., The rise in vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium in Germany: data from the German Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance (ARS). Antimicrob Resist Infect Control, 2019. 8: p. 147
- Tacconelli, E., et al., Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: the WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. Lancet Infect Dis, 2018. 18(3): p. 318-327.
- Said, H.S. and E.S. Abdelmegeed, Emergence of multidrug resistance and extensive drug resistance among enterococcal clinical isolates in Egypt. Infect Drug Resist, 2019. 12: p. 1113-1125.
- Remschmidt, C., et al., Continuous increase of vancomycin resistance in enterococci causing nosocomial infections in Germany – 10 years of surveillance. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control, 2018. 7: p. 54